
Next.js vs React : Which one to Choose in 2026?
Next.js and React are often compared when teams choose a front-end stack. This comparison exists because both are used to build React-based applications, but they serve different scopes.
React is an open-source JavaScript library for building UIs. It is sufficient when an application only needs client-side rendering and custom architecture. Many applications do not require server rendering, routing conventions, or framework-level abstractions.
Next.js builds on React and adds an application framework. It provides routing, rendering strategies, data fetching, and production defaults. These features are useful when applications become more complex or require server-side capabilities.
The choice is not about full-stack versus simple applications. It is about how much responsibility the framework should handle versus how much the team wants to manage manually.
This article explains when React alone is sufficient and when Next.js becomes necessary. It focuses on architecture, rendering behavior, and real production trade-offs.
What is Next.js?
Next.js is an open-source React framework developed by Vercel for building production web applications.
It supports two routing systems: the App Router for modern applications and the Pages Router for legacy and compatibility use cases.
The framework defaults to a server-first approach, offering support for server-side rendering, static generation, incremental static regeneration, and streaming.
Routing is defined through the file system. The App Router uses the app/ directory. The Pages Router uses the pages/ directory.
Next.js includes backend primitives. The App Router exposes Route Handlers and Server Actions. The Pages Router exposes API Routes.
The framework automatically applies performance optimizations, including code splitting, image and font optimization, and built-in caching.
Next.js:
- Original Author: Guillermo Rauch
- Written in: JavaScript (React)
- Initial Release: October 25, 2016
- Developers: Vercel (formerly ZEIT) and the Next.js community
- Platform: Web Platform
- Website: https://nextjs.org/
- License: MIT License
- Type: JavaScript Framework
Summary: Next.js extends React with routing, rendering, and server capabilities for production applications.
What is React?
React is an open-source JavaScript library developed by Meta for building user interfaces.
It defines how elements are rendered and updated. But it does not define routing, data fetching, or application structure.
Moreover, React uses a component-based model. Components encapsulate UI, state, and behavior, enabling reuse and predictable rendering.
It optimizes updates through a virtual DOM. It computes minimal changes and applies them to the browser DOM efficiently.
Primarily run on the client side. Server rendering is possible but requires external frameworks or tooling.
React integrates with libraries for routing, state management, and data handling. These choices are left to the development team.
React:
- Original Author: Jordan Walke
- Written in: JavaScript
- Initial Release: May 29, 2013
- Developers: Meta (Formerly Facebook) and the React community
- Platform: Web
- Website: https://react.dev/
- License: MIT License
- Type: JavaScript Library
Summary: React provides the UI rendering layer. It leaves application architecture and infrastructure decisions to the developer.
React vs. Next.js
React and Next.js serve different roles in the React ecosystem. Comparing them requires understanding the scope, responsibility, and execution model.
Below is a practical comparison based on architecture and production behavior.
[Infographics ( Next.js vs. React)]
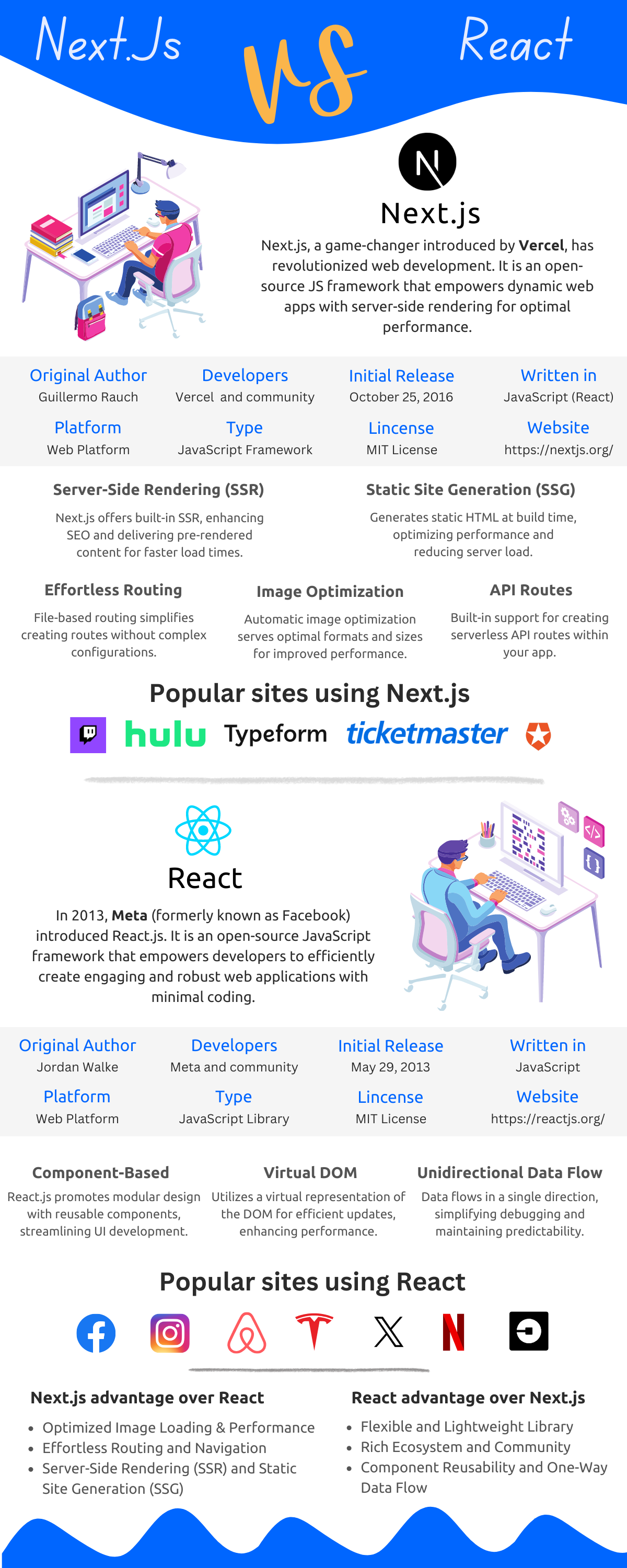
Here's a detailed comparison between React and Next.js:
Scope and Responsibility
- React: Defines how user interfaces are composed and updated. It focuses on the view layer only.
- Next.js: Defines how a React application is structured, rendered, and deployed. It provides framework-level defaults.
Rendering
- React: Renders primarily on the client. Server rendering requires external frameworks or a custom setup.
- Next.js: Uses a server-first rendering model. Supports server-side rendering, static generation, incremental regeneration, and streaming.
Routing
- React: Does not include routing. Teams integrate routing libraries and define navigation manually.
- Next.js: Includes built-in routing. Routes are derived from the file system using either the App Router or Pages Router.
Data Fetching
- React: Does not define data fetching behavior. Developers manage requests, caching, and synchronization manually.
- Next.js: Integrates data fetching with rendering. Fetching supports caching, revalidation, and server execution by default.
Backend Capabilities
- React: Does not include backend primitives. APIs and server logic live outside the React application.
- Next.js: Includes backend features. Route Handlers, Server Actions, and API routes enable server logic to be implemented within the same codebase.
Performance Defaults
- React: Performance depends on application architecture and manual optimization.
- Next.js: Automatically applies performance optimizations, including code splitting, image optimization, font optimization, and caching.
Application Structure
- React: Leaves structure decisions to the team. No enforced conventions.
- Next.js: Enforces conventions for routing, layouts, loading states, and error handling through file-system rules.
Deployment Model
- React: Requires a custom build and deployment configuration depending on the stack.
- Next.js: Ships with a defined build and runtime model. Supports Node.js, Edge, and static output targets.
When to Use Each
Use React when:
- The application is client-rendered
- Architecture needs full customization
- Backend and routing are handled separately
Use Next.js when:
- Server rendering or static generation is required
- Routing and data fetching should be framework-managed
- Production defaults and performance matter
Summary: React provides the UI layer. Next.js provides the application framework. The choice depends on how much responsibility the framework should own versus the development team.
Overview of Next.js vs. React
Below is a comparison table for a brief overview of Next.js vs React:
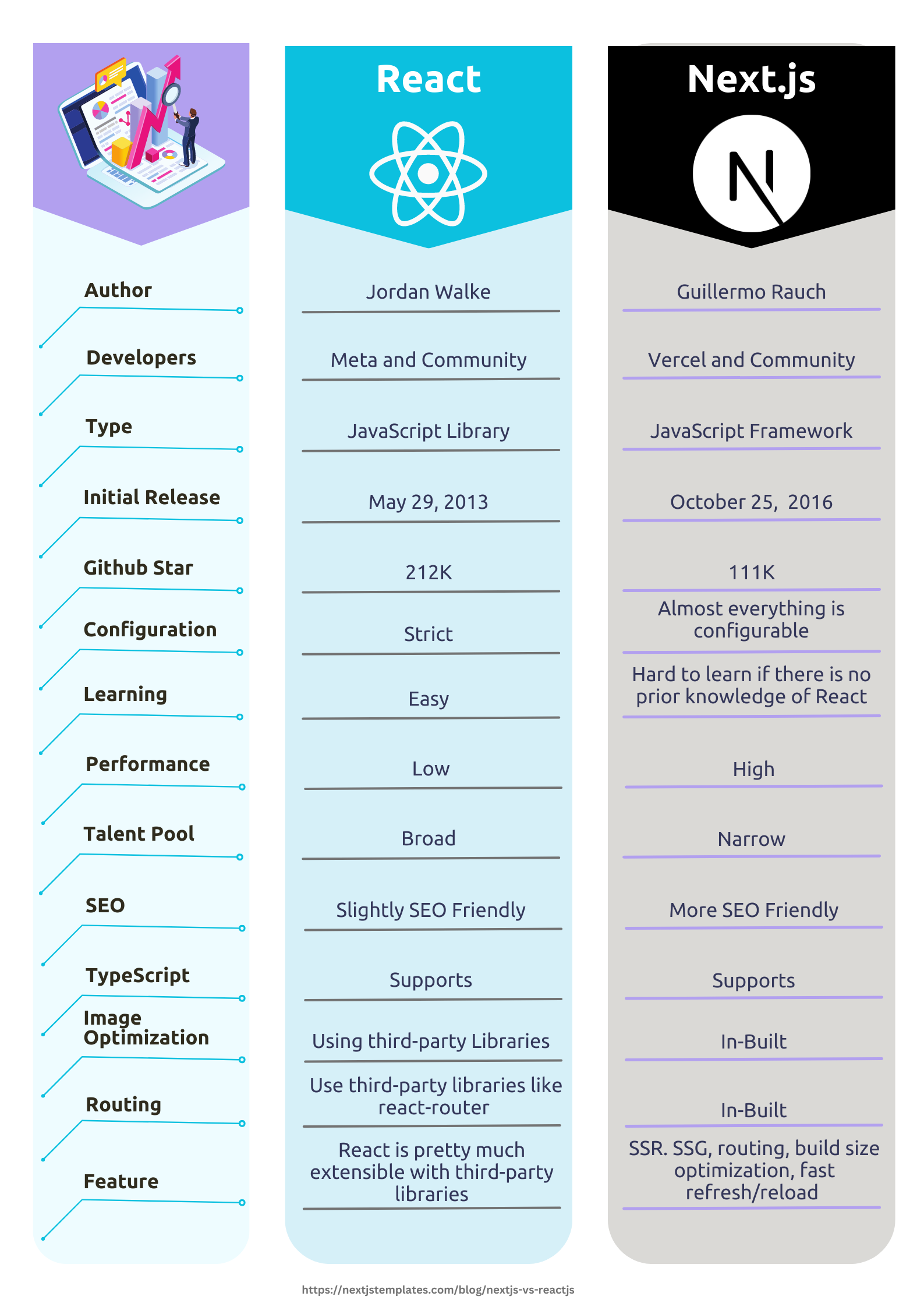
Advantages of Next.js
Next.js provides framework-level capabilities that address rendering, data, and performance.
1. Integrated Rendering
- Supports Server-Side Rendering (SSR) for request-time HTML generation
- Supports Static Site Generation (SSG) for build-time HTML output
- Supports Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR) for background updates after deployment
- Supports Streaming with Suspense for partial page rendering
- Allows rendering strategy to be defined per route, not per application
- Eliminates the need for separate SSR frameworks or build pipelines
Impact: Improves first-load performance, cache control, and SEO without custom infrastructure.
2. Built-in Routing and Navigation
- Uses file-system routing instead of manual route configuration
- Supports both App Router (layouts, nested routing, streaming) and Pages Router (page-based routing)
- Enables dynamic routes, catch-all routes, and optional segments
- Handles layouts, loading UI, error boundaries, and not-found states at the routing level
- Removes dependency on third-party routing libraries
Impact: Reduces routing complexity and enforces consistent navigation patterns.
3. Data Fetching
- Executes data fetching on the server by default
- Extends fetch() with automatic caching, request deduplication, and revalidation
- Supports time-based, path-based, and tag-based cache invalidation
- Prevents client-side waterfall requests
- Aligns data lifecycle with route rendering
Impact: Predictable data behavior with fewer performance pitfalls.
4. Unified Frontend and Backend Model
- Allows backend logic inside the same codebase as UI
- App Router provides Route Handlers and Server Actions
- Pages Router provides API Routes
- Supports Node and Edge runtimes per route
- Removes the need for a separate BFF in many applications
Impact: Simplifies architecture and deployment for full-stack React apps.
5. Performance
- Automatic code splitting per route and component
- Built-in image optimization with responsive sizing and formats
- Built-in font optimization with zero layout shift
- Framework-managed caching and revalidation
- Minimal production configuration required
Impact: Performance optimizations are applied consistently without manual tuning.
6. Companies Using Next.js
- Used for applications requiring server rendering, SEO, and structured routing
- Examples: Twitch, Hulu, Ticketmaster, Typeform, Auth0, Cred, Gitpod, Hudl
Advantages of React
React provides a minimal, unopinionated UI layer that prioritizes control over convention.
1. Minimal Abstraction and Control
- Provides only the UI rendering layer
- Does not enforce routing, data fetching, or deployment models
- Leaves architectural decisions entirely to the team
Impact: Ideal for applications with strict infrastructure or platform constraints.
2. Flexibility in Architecture
- Works with any router, state manager, or data layer
- Integrates into existing backend systems easily
- Supports custom build tools and deployment workflows
Impact: Suitable for highly customized or embedded applications.
3. Component-Centric
- Encourages reusable, isolated UI components
- Supports predictable one-way data flow
- Enables fine-grained control over rendering behavior
Impact: Scales well for complex UI systems when the architecture is managed carefully.
4. Mature and Stable Ecosystem
- Backed by long-term community and enterprise adoption
- Wide availability of libraries, tooling, and patterns
- Stable API surface with gradual evolution
Impact: Lower risk for long-lived applications.
5. Companies Using React
- Used for large-scale client-rendered and hybrid applications
- Examples: Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp Web, Reddit, Netflix, Airbnb, Uber, Dropbox, Pinterest, X
Which One Should You Choose in 2026?
The choice between React and Next.js depends on the application's requirements, not personal preference.
Choose React when:
- The application is primarily client-rendered
- Routing, data fetching, and backend logic are handled separately
- The architecture requires full customization
- The project integrates into an existing platform or backend
- Bundle size and framework overhead must remain minimal
Choose Next.js when:
- Server-side rendering or static generation is required
- SEO and initial load performance are important
- Routing and data fetching should follow framework conventions
- Backend logic should live alongside UI code
- The application needs production-ready defaults
Both tools are good in their own right in 2026. They solve different problems at different layers of the stack.
Conclusion
React and Next.js are not competitors. React provides the UI rendering layer. Next.js provides the application framework around React.
React works best when teams want full architectural control. Next.js works best when teams want structure, performance, and production defaults.
The correct choice depends on how much responsibility the framework should manage versus how much the team is willing to handle manually.
Related Articles
Musharof
Compatibility Issues with Next.js 15: npm install --legacy-peer-deps
You may have noticed that we've already updated all our templates to Next.js 15. While this puts us slightly ahead of th
Read MoreMusharof
All templates, boilerplates, and starter kits are now updated to Next.js 16.0.10
We’re excited to announce an important upgrade for our Next.js Templates users. All templates available on Next.js
Read MoreSumaiya Afrin Kanak
7+ Best AI Website Templates for 2026 - Agents, Chatbots, Starter Kits
Do you know what the new trend is in building an AI website ? You must have guessed it by now! Yes, it is the AI websit
Read More

