
Next.js vs Nuxt: Which one is Better in 2026?
Next.js and Nuxt are frequently compared when teams evaluate modern web frameworks. This comparison exists because both frameworks target production-ready applications.
Next.js extends React with framework-level features. In contrast, Nuxt extends Vue.js with a similar application model.
As a result, both frameworks address common needs such as routing, rendering, data handling, and deployment defaults. However, they implement these concerns using different architectural decisions.
Because of this, choosing between them is not a matter of popularity. Instead, it depends on ecosystem alignment, rendering requirements, and operational constraints.
Therefore, this article compares Next.js and Nuxt from a technical perspective. It focuses on rendering models, routing systems, backend integration, and performance behavior.
Ultimately, the objective is to help teams make informed decisions based on real production needs.
What is Next.js?
Next.js is an open-source application framework built on top of React and maintained by Vercel.
It defines application structure, routing, rendering, and deployment behavior. As a result, teams do not need to assemble separate dependencies for production.
Next.js supports two routing systems. The App Router is the modern default, while the Pages Router remains supported for compatibility.
The framework follows a server-first rendering model. It supports server-side rendering, static generation, incremental static regeneration, and streaming.
Rendering behavior is configured per route. This enables the coexistence of static and dynamic content within the same application.
Routing is file-system-based. Routes are created by placing files inside the app/ or pages/ directories.
Next.js includes backend primitives. The App Router provides Route Handlers and Server Actions, while the Pages Router provides API Routes.
Performance optimizations are enabled by default. These include code splitting, image optimization, font optimization, and built-in caching.
These patterns are commonly implemented in production-ready Next.js templates, which demonstrate real-world routing, rendering, and performance setups.
Next.js:
- Original Author: Guillermo Rauch
- Written in: JavaScript (React)
- Initial Release: October 25, 2016
- Developers: Vercel (formerly ZEIT) and the Next.js community
- Platform: Web Platform
- Website: nextjs.org
- License: MIT License
- Type: JavaScript Framework
- GitHub Repository: Github.com/vercel/next.js
- Current Version: Next.js 16
In Summary, Next.js extends React with routing, rendering, and server capabilities. It targets production applications that require structure, performance, and predictable behavior.
Let's explore another option, Nuxt, which is created for Vue.js applications.
What is Nuxt?

Nuxt is an open-source application framework built on top of Vue.js. It is maintained by the Nuxt team and the Vue ecosystem.
Similar to Next.js for React, Nuxt defines the structure, rendering, and deployment of a Vue application. As a result, it removes the need to assemble separate production tools.
Nuxt follows a server-first architecture powered by Nitro. It supports server-side rendering, static generation, hybrid rendering, and edge deployment.
Routing is handled through file-system conventions. Routes are generated automatically from the directory structure.
Nuxt integrates data fetching with rendering. Server data runs during rendering and supports caching and revalidation.
Backend logic runs inside the same project. Nitro provides server endpoints that work across Node, serverless, and edge runtimes.
Nuxt applies performance optimizations by default. These include code splitting, automatic imports, optimized asset handling, and runtime caching.
The framework uses opinionated defaults. This enforces consistency and reduces the need for architectural decisions during the development process.
Nuxt
- Original Author: Sebastien Chopin and Alexandre Chopin
- Written in: JavaScript (Vue.js)
- Initial Release: October 26, 2016
- Developers: Nuxt and Vue.js community
- Platform: Cross Platform
- Website: Nuxtjs.org
- License: MIT License
- Type: JavaScript Framework
- GitHub Repository: Github.com/nuxt/nuxt
- Current Version: Nuxt 4
In summary, Nuxt extends Vue.js with routing, rendering, and backend capabilities. It targets structured, production-ready applications with built-in performance defaults and consistent conventions.
Now, let's compare Next.js and Nuxt in detail.
Next.js vs. Nuxt
Next.js and Nuxt serve the same role in different ecosystems. Both turn a UI library into a full application framework.
Because of this shared purpose, both frameworks solve similar problems. These include routing, rendering, data handling, and deployment.
However, they solve these problems using different design choices. As a result, teams face different trade-offs.
[Infographics Comparison ( Next.js vs. Nuxt)]
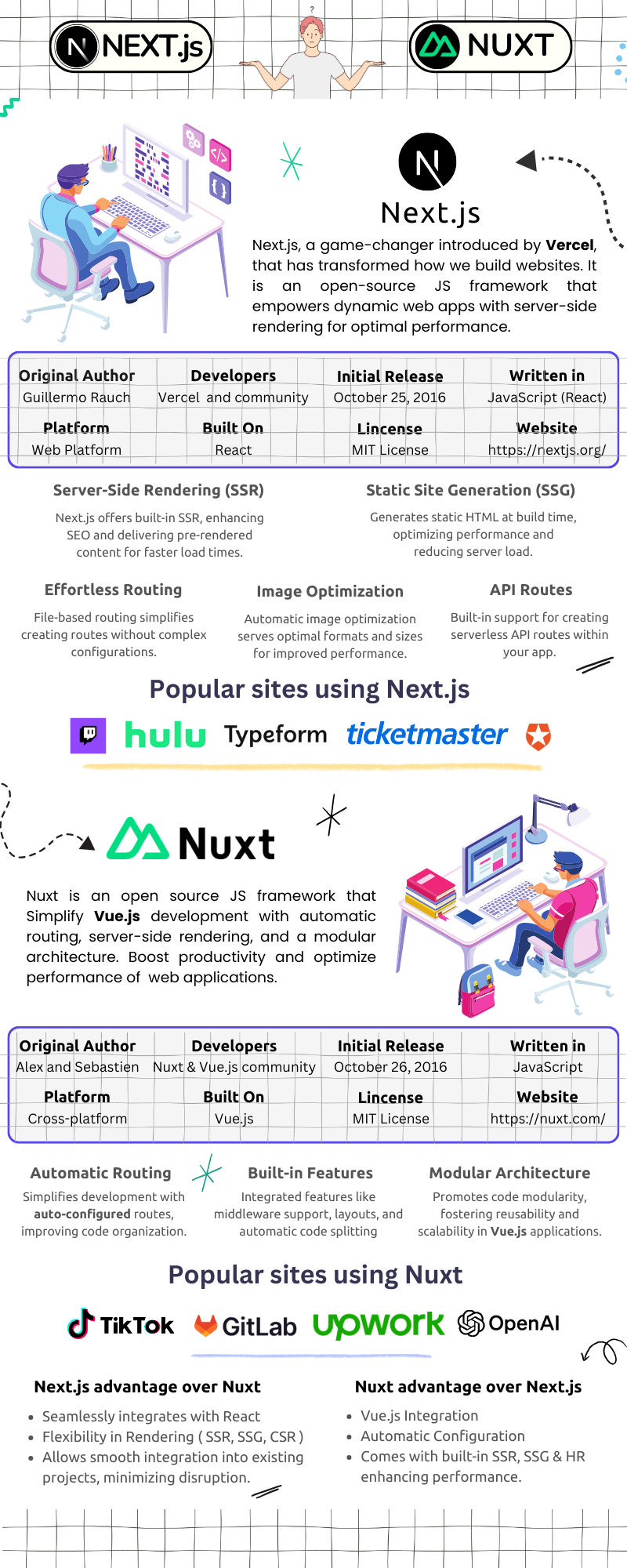
Here's a detailed comparison between Nuxt and Next.js:
Framework Scope
- Nuxt is the application framework for Vue.js. It defines how Vue applications are structured and deployed.
- Next.js is the application framework for React. It defines how React applications are built and shipped to production.
Rendering Model
- Nuxt follows a server-first architecture powered by Nitro. It supports server rendering, static generation, hybrid rendering, and edge execution.
- Next.js also uses a server-first model. It supports server rendering, static generation, incremental regeneration, and streaming.
Routing System
- Nuxt uses file-based routing by default. Routes are created automatically from the folder structure.
- Next.js also uses file-based routing. It supports the App Router for modern apps and the Pages Router for compatibility.
Data Fetching
- Nuxt runs data fetching during rendering. Server data supports caching and revalidation.
- Next.js integrates data fetching into rendering. Fetch requests support caching, deduplication, and revalidation.
Backend Integration
- Nuxt includes backend logic through Nitro endpoints. These endpoints run across Node, serverless, and edge environments.
- Next.js includes backend features through Route Handlers, Server Actions, and API Routes. The available options depend on the router.
Performance Defaults
- Nuxt applies performance optimizations automatically. These include code splitting, auto imports, and runtime caching.
- Next.js also applies performance optimizations by default. These include code splitting, image optimization, font optimization, and caching.
Configuration Approach
- Nuxt follows opinionated conventions. These defaults reduce setup decisions and enforce consistency.
- Next.js provides strong defaults but allows overrides. Teams can adjust behavior when needed.
Deployment Targets
- Nuxt supports Node, serverless, edge, and static output. Deployment is managed through Nitro adapters.
- Next.js supports Node, Edge Runtime, and static output. It also integrates closely with Vercel.
Ecosystem Alignment
- Nuxt aligns with the Vue.js ecosystem. Patterns and tools follow Vue conventions.
- Next.js aligns with the React ecosystem. Patterns and tools follow React conventions.
Learning Curve
- Nuxt is easier for teams familiar with Vue. The framework reinforces Vue patterns.
- Next.js is easier for teams familiar with React. The framework builds on React concepts.
Documentation Focus
- Nuxt documentation emphasizes conventions and defaults. It guides teams toward a consistent setup.
- Next.js documentation emphasizes rendering behavior and production patterns. It explains trade-offs and configuration.
In Summary, Nuxt and Next.js address the same application needs. They differ in structure, flexibility, and ecosystem fit.
Nuxt favors consistency and convention. Next.js favors flexibility with strong defaults.
The right choice depends on the UI library, team experience, and production requirements.
Advantages of Next.js
- React Ecosystem Alignment: Next.js is built specifically for React. It integrates directly with the React ecosystem, including tooling, libraries, and established patterns.
- Flexible Rendering Control: Next.js enables the definition of rendering strategies per route. Teams can mix server rendering, static generation, incremental regeneration, and streaming within one application.
- Advanced Data Fetching Model: Next.js extends the native fetch API with caching, revalidation, and request deduplication. Data fetching is closely tied to rendering behavior.
- Backend Capabilities Inside the Framework: Next.js provides backend primitives through Route Handlers, Server Actions, and API Routes.
- Deployment and Platform Integration: Next.js integrates deeply with Vercel. The platform offers optimized builds, edge execution, and global caching with minimal configuration requirements.
- Companies Using Next.js: Next.js is used by organizations that require server rendering, SEO, and performance at scale.
- Examples include Loom, The Washington Post, Notion, Hulu, Twitch, Tencent News, Nike, and Typeform.
Advantages of Nuxt
- Vue-First Design: Nuxt is designed exclusively for Vue.js. It follows Vue conventions and reinforces Vue patterns across routing, dat, fetching, and state handling.
- Opinionated Structure: Nuxt enforces a consistent project structure through conventions. Routing, layouts, and configuration follow predictable patterns.
- Nitro-Powered Backend: Nuxt includes backend logic through Nitro. Server endpoints run across Node, serverless, and edge environments without changes.
- Built-in Modularity: Nuxt supports a module system for extending functionality. Common concerns, such as authentication, analytics, and CMS integration, are addressed through modules.
- Automatic Imports: Nuxt supports automatic imports for components, composables, and utilities.
- Companies Using Nuxt: Nuxt is used by organizations building Vue-based production applications.
- Examples include Upwork, OpenAI, TikTok, GitLab, CDNJS, Fox News, BitPay, and Unilever.
In Summary, Next.js and Nuxt solve similar problems at the framework level. Their advantages reflect different design goals.
Next.js prioritizes flexibility and deep React integration. Nuxt prioritizes convention and a guided Vue-first experience.
The correct choice depends on ecosystem alignment, team preference, and production requirements.
Which One Should You Choose in 2026?
The choice between Next.js and Nuxt depends on the application's requirements, not the framework's popularity.
Both frameworks solve similar problems. However, they optimize for different ecosystems and development models.
Choose Next.js when:
- The application is built with React
- Server-side rendering, static generation, or streaming is required
- Rendering and data fetching should be controlled at the route level
- Backend logic should live alongside UI code
- Flexibility and fine-grained control are important
Next.js is especially effective for dashboards, SaaS products, and admin interfaces, where teams often start from production-ready Next.js dashboard templates or Next.js boilerplates to accelerate development while retaining architectural control.
Choose Nuxt when:
- The application is built with Vue.js
- Convention-based structure is preferred
- Backend logic should work across Node, serverless, and edge runtimes
- Faster setup with fewer architectural decisions is important
- Team consistency matters more than customization
Nuxt works best for teams that value guided patterns and predictable structure.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why choose Nuxt instead of using Vue alone?
Nuxt should be used in conjunction with Vue when an application requires routing, server rendering, backend endpoints, and deployment defaults. Vue only defines the UI layer, while Nuxt provides a complete application framework. This removes the need to manually assemble tools for routing, SSR, data fetching, and production builds.
2. Why choose Next.js instead of using React alone?
Next.js should be used in conjunction with React when an application requires routing, server-side rendering, SEO support, or backend integration. React handles UI rendering only. Next.js defines how the application is structured, rendered, and deployed in production.
3. What problem do Next.js and Nuxt solve?
Next.js and Nuxt solve the problem of turning a UI library into a production-ready application. They provide conventions for routing, rendering strategies, data handling, and deployment. This reduces architectural uncertainty and improves consistency across environments.
4. How do Next.js and Nuxt differ at a high level?
Next.js emphasizes flexibility and granular control, while Nuxt emphasizes convention and guided structure. Both solve the same problems, but they make different trade-offs based on the design principles of the React and Vue ecosystems.
5. Which framework is easier to adopt?
Next.js is easier to adopt for teams already experienced with React. Nuxt is easier to adopt for teams already experienced with Vue. Neither framework introduces a new programming model beyond its underlying UI library.
6. When does Nuxt make more sense than Next.js?
Nuxt makes more sense when a Vue-based team wants a structured, opinionated framework with minimal architectural decisions. It is well-suited for teams that prefer conventions over configuration.
7. When does Next.js make more sense than Nuxt?
Next.js makes more sense when a React-based team requires flexible rendering strategies, backend logic within the same codebase, and fine-grained control over application behavior.
8. Are Next.js and Nuxt suitable for large applications?
Both frameworks are designed for large-scale production use. They support modular architectures, server rendering, and long-term maintenance, and they are widely adopted by enterprise teams.
9. Is one framework more future-proof than the other?
Neither framework is inherently more future-proof. Longevity depends on continued React or Vue ecosystem adoption rather than framework capability. Both are actively maintained and aligned with platform evolution.
Conclusion
Next.js and Nuxt are not competitors. They are solutions for different ecosystems.
Next.js provides a flexible React-based application framework with strong production defaults. Whereas Nuxt provides a structured Vue-based application framework with opinionated conventions.
The best framework is the one that fits the team, the ecosystem, and the production requirements.
Choose based on responsibility, not preference.
Related Articles
Musharof
Compatibility Issues with Next.js 15: npm install --legacy-peer-deps
You may have noticed that we've already updated all our templates to Next.js 15. While this puts us slightly ahead of th
Read MoreMusharof
All templates, boilerplates, and starter kits are now updated to Next.js 16.0.10
We’re excited to announce an important upgrade for our Next.js Templates users. All templates available on Next.js
Read MoreSumaiya Afrin Kanak
7+ Best AI Website Templates for 2026 - Agents, Chatbots, Starter Kits
Do you know what the new trend is in building an AI website ? You must have guessed it by now! Yes, it is the AI websit
Read More

